Top Links:  >> 80. Technology >> Internet Technology Summit Program >> 3. Threads and Network >> 3.2. Network
>> 80. Technology >> Internet Technology Summit Program >> 3. Threads and Network >> 3.2. Network
Current Topic: 3.2.4. Server Socket providing services
package its.day15.sockets;
/**
* The ItsBaseService interface is a blueprint for simple service classes with the run() method
* @author Jeff.Zhuk@Javaschool.com
*/
public interface ItsBaseService {
public String run(String params);
}
package its.day15.sockets;
public class RequestRepetitionService implements ItsBaseService {
@Override
public String run(String params) {
return params + " - from server!";
}
}
package its.day15.sockets;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* The ServerSocketService class opens a ServerSocket on a localhost at an assigned port
* The server socket will be responding to client requests by calling one of existing services
* All services implement the ItsBaseService interface
* @author Jeff.Zhuk@Javaschool.com
*
*/
public class ServerSocketService {
/**
* This is a simple server socket that provide requested services.
* The server socket will start at the assigned port number and will be waiting for requests from clients.
* Upon receiving the client request the server socket will create an internal socket to collaborate with the client.
* The internal socket will open Input and Output streams.
* Then the method expects to receive a string from a client with the instructions on a requested service.
* A string-instruction must include a service class name and a string-parameter separated by the "|" character
* Example: its.day15.sockets.RequestRepetitionService|Hello
* The service class must implement the ItsBaseService interface with the run() method.
* The server socket will instantiate the server class and run the service.
* The run() method will return a string.
* The server socket will send this string back to the client via the Output stream.
* Then the server will close the streams and the internal socket.
* It will continue waiting for more requests from the clients.
*
* @param portNumber
*/
public void serverSocketService(int portNumber) {
boolean stopTheProcess = false;
ServerSocket server = null;
// register server socket on the portNumber
try {
server = new ServerSocket(portNumber);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Server socket failure: " + e);
return;
}
// start a loop waiting for client requests
while (!stopTheProcess) {
// make client request, socket and stream objects available for exception cases
String clientRequest = null;
Socket socket = null;
DataOutputStream dos = null;
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
// listen for a client request and accept the request from a
// client with creating a local socket
socket = server.accept();
// connect input/output streams to the socket
OutputStream outStream = socket.getOutputStream();
InputStream inStream = socket.getInputStream();
// transform into DataInputStream and DataOutputStream to use UTF strings
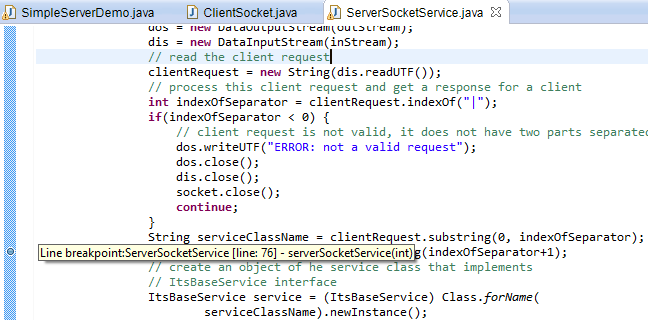
dos = new DataOutputStream(outStream);
dis = new DataInputStream(inStream);
// read the client request
clientRequest = new String(dis.readUTF());
// process this client request and get a response for a client
int indexOfSeparator = clientRequest.indexOf("|");
if(indexOfSeparator < 0) {
// client request is not valid, it does not have two parts separated by "|"
dos.writeUTF("ERROR: not a valid request");
dos.close();
dis.close();
socket.close();
continue;
}
String serviceClassName = clientRequest.substring(0, indexOfSeparator);
String params = clientRequest.substring(indexOfSeparator+1);
// create an object of he service class that implements
// ItsBaseService interface
ItsBaseService service = (ItsBaseService) Class.forName(
serviceClassName).newInstance();
// invoke the implemented run() method and get the response
String response = service.run(params);
dos.writeUTF(response); // success or failure
// close the client connection, keep alive the server socket
socket.close();
stopTheProcess = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// exception with one client will not stop server from serving other clients
String response = "ERROR: Server socket failure: " + e + " on the clientRequest="+clientRequest;
if(dos != null) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(response);
dos.close();
dis.close();
socket.close();
} catch(Exception dosException) {
System.out.println(dosException);
}
}
System.out.println(response);
stopTheProcess = true;
}
}
}
/**
* This test will start the server socket on localhost at the portNumber and be waiting for client requests
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocketService server = new ServerSocketService();
server.serverSocketService(5555);
}
}
<br/>package its.day15.sockets;
<br/>/**
<br/> * The ItsBaseService interface is a blueprint for simple service classes with the run() method
<br/> * @author Jeff.Zhuk@Javaschool.com
<br/> */
<br/>public interface ItsBaseService {
<br/> public String run(String params);
<br/>}
<br/>
<br/>package its.day15.sockets;
<br/>
<br/>public class RequestRepetitionService implements ItsBaseService {
<br/>
<br/> @Override
<br/> public String run(String params) {
<br/> return params + " - from server!";
<br/> }
<br/>
<br/>}
<br/>
<br/>package its.day15.sockets;
<br/>
<br/>import java.io.DataInputStream;
<br/>import java.io.DataOutputStream;
<br/>import java.io.IOException;
<br/>import java.io.InputStream;
<br/>import java.io.OutputStream;
<br/>import java.net.ServerSocket;
<br/>import java.net.Socket;
<br/>/**
<br/> * The ServerSocketService class opens a ServerSocket on a localhost at an assigned port
<br/> * The server socket will be responding to client requests by calling one of existing services
<br/> * All services implement the ItsBaseService interface
<br/> * @author Jeff.Zhuk@Javaschool.com
<br/> *
<br/> */
<br/>public class ServerSocketService {
<br/> /**
<br/> * This is a simple server socket that provide requested services.
<br/> * The server socket will start at the assigned port number and will be waiting for requests from clients.
<br/> * Upon receiving the client request the server socket will create an internal socket to collaborate with the client.
<br/> * The internal socket will open Input and Output streams.
<br/> * Then the method expects to receive a string from a client with the instructions on a requested service.
<br/> * A string-instruction must include a service class name and a string-parameter separated by the "|" character
<br/> * Example: its.day15.sockets.RequestRepetitionService|Hello
<br/> * The service class must implement the ItsBaseService interface with the run() method.
<br/> * The server socket will instantiate the server class and run the service.
<br/> * The run() method will return a string.
<br/> * The server socket will send this string back to the client via the Output stream.
<br/> * Then the server will close the streams and the internal socket.
<br/> * It will continue waiting for more requests from the clients.
<br/>
<br/> *
<br/> * @param portNumber
<br/> */
<br/> public void serverSocketService(int portNumber) {
<br/> boolean stopTheProcess = false;
<br/> ServerSocket server = null;
<br/> // register server socket on the portNumber
<br/> try {
<br/> server = new ServerSocket(portNumber);
<br/> } catch (IOException e) {
<br/> System.out.println("Server socket failure: " + e);
<br/> return;
<br/> }
<br/> // start a loop waiting for client requests
<br/> while (!stopTheProcess) {
<br/> // make client request, socket and stream objects available for exception cases
<br/> String clientRequest = null;
<br/> Socket socket = null;
<br/> DataOutputStream dos = null;
<br/> DataInputStream dis = null;
<br/> try {
<br/> // listen for a client request and accept the request from a
<br/> // client with creating a local socket
<br/> socket = server.accept();
<br/> // connect input/output streams to the socket
<br/> OutputStream outStream = socket.getOutputStream();
<br/> InputStream inStream = socket.getInputStream();
<br/> // transform into DataInputStream and DataOutputStream to use UTF strings
<br/> dos = new DataOutputStream(outStream);
<br/> dis = new DataInputStream(inStream);
<br/> // read the client request
<br/> clientRequest = new String(dis.readUTF());
<br/> // process this client request and get a response for a client
<br/> int indexOfSeparator = clientRequest.indexOf("|");
<br/> if(indexOfSeparator < 0) {
<br/> // client request is not valid, it does not have two parts separated by "|"
<br/> dos.writeUTF("ERROR: not a valid request");
<br/> dos.close();
<br/> dis.close();
<br/> socket.close();
<br/> continue;
<br/> }
<br/> String serviceClassName = clientRequest.substring(0, indexOfSeparator);
<br/> String params = clientRequest.substring(indexOfSeparator+1);
<br/> // create an object of he service class that implements
<br/> // ItsBaseService interface
<br/> ItsBaseService service = (ItsBaseService) Class.forName(
<br/> serviceClassName).newInstance();
<br/> // invoke the implemented run() method and get the response
<br/> String response = service.run(params);
<br/> dos.writeUTF(response); // success or failure
<br/> // close the client connection, keep alive the server socket
<br/> socket.close();
<br/> stopTheProcess = true;
<br/> } catch (Exception e) {
<br/> // exception with one client will not stop server from serving other clients
<br/> String response = "ERROR: Server socket failure: " + e + " on the clientRequest="+clientRequest;
<br/> if(dos != null) {
<br/> try {
<br/> dos.writeUTF(response);
<br/> dos.close();
<br/> dis.close();
<br/> socket.close();
<br/> } catch(Exception dosException) {
<br/> System.out.println(dosException);
<br/> }
<br/> }
<br/> System.out.println(response);
<br/> stopTheProcess = true;
<br/> }
<br/> }
<br/> }
<br/> /**
<br/> * This test will start the server socket on localhost at the portNumber and be waiting for client requests
<br/> * @param args
<br/> */
<br/> public static void main(String[] args) {
<br/> ServerSocketService server = new ServerSocketService();
<br/> server.serverSocketService(5555);
<br/> }
<br/>}
<br/>


